Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectrometer (Optima 7300 DV Perkin Elmer)Principle: The sample is aspirated to the spray chamber where it passes through a nebulizer and is converted into an aerosol and carried to the plasma by argon flow. Once in the plasma, the atoms and ions in the sample are excited to emit light at a wavelength characteristic of the element (spectra) by a radio-frequency source and the inductively coupled plasma. The spectra are dispersed by a grating spectrometer, and the intensities of the line spectra are monitored at specific wavelengths by a photosensitive solid-state detector. Emitted light energy is converted to electrical signals, digitized and collected by the computer. By calibrating the instrument with a solution containing each analyte at a known concentration, the sample data is compared to the calibration data by the instrument software resulting in a quantitative result for each analyte in the sample. Applications: Soils, sediments, sludges, and aqueous samples including groundwater, surface water and seawater, biological samples including fish and plant tissue, and air filter can be analyzed. |
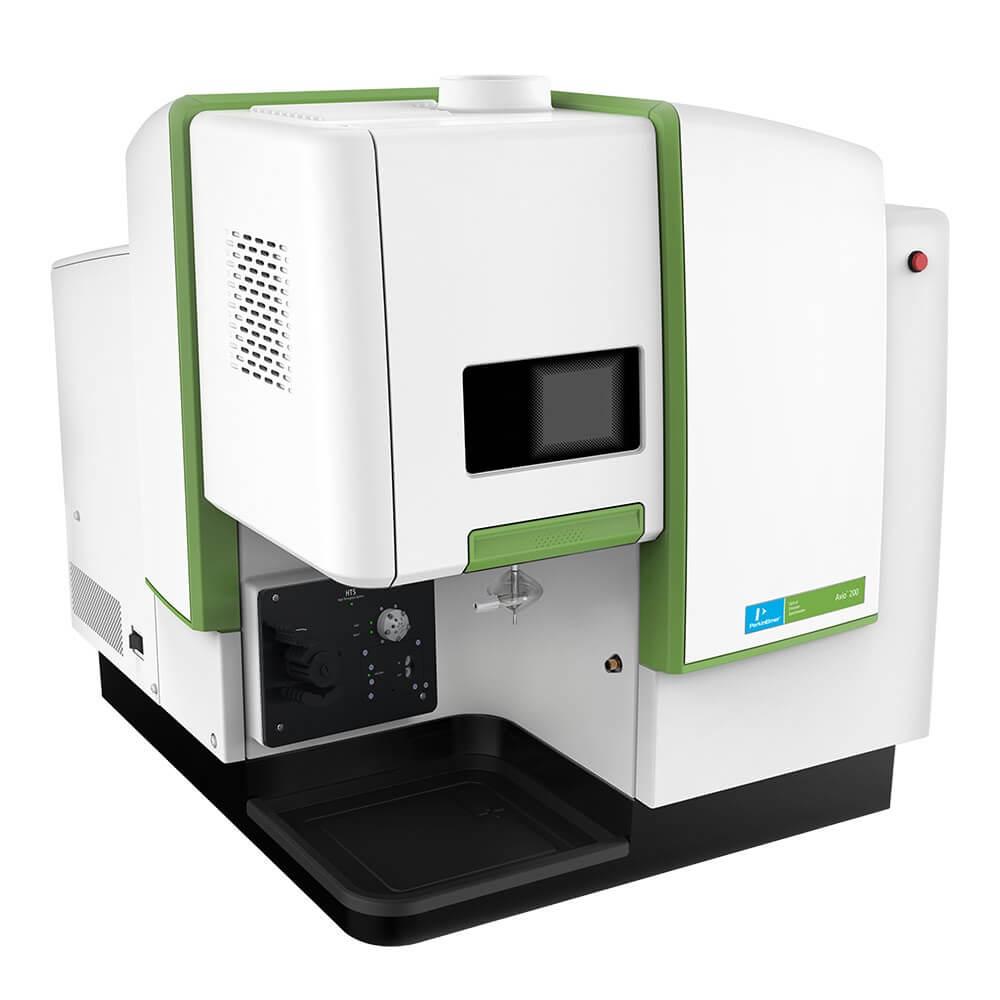
Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectrometer (AVIO 200)Principle: The sample is aspirated to the spray chamber where it passes through a nebulizer and is converted into an aerosol and carried to the plasma by argon flow. Once in the plasma, the atoms and ions in the sample are excited to emit light at a wavelength characteristic of the element (spectra) by a radio-frequency source and the inductively coupled plasma. The spectra are dispersed by a grating spectrometer, and the intensities of the line spectra are monitored at specific wavelengths by a photosensitive solid-state detector. Emitted light energy is converted to electrical signals, digitized and collected by the computer. By calibrating the instrument with a solution containing each analyte at a known concentration, the sample data is compared to the calibration data by the instrument software resulting in a quantitative result for each analyte in the sample. Applications: Soils, sediments, sludges, and aqueous samples including groundwater, surface water and seawater, biological samples including fish and plant tissue, and air filter and organic samples such as oil and petroleum products can be analyzed. |
Image  Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) – (Velp Scientifica)Principle: The test consists of introducing a sample, or dilution thereof, into an airtight BOD bottle and incubating the bottle in the dark for a specified time (5 days) and temperature (20°C). Dissolved oxygen (DO) is measured at the beginning and at the end of the incubation period and 5-day BOD is calculated as the difference between the two expressed as milligrams oxygen per liter. BOD is a biological process, and a sufficient population of bacteria must be present in the sample being analyzed. To insure this, samples or dilutions are seeded with a known amount of bacterial inoculum Applications: The Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) test is an empirical bioassay for waters and wastewaters. |
Image  Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) – (NANOCOLOR VIS II)Principle: When a Sample is digested the dichromate ion oxidizes the COD material in the sample, this results in the change of chromium from the hexavalent state to trivalent state. Both of these chromium species are colored and absorbs in the visible region of the spectrum. The dichromate ion absorbs strongly in 400 nm region, where the chromic ion absorption is much less. The COD value of 90mg/l or less can be determined by following the decrease in Cr2 O72- 420 nm. Applications: Used for the examination of water and waste water and soil. |
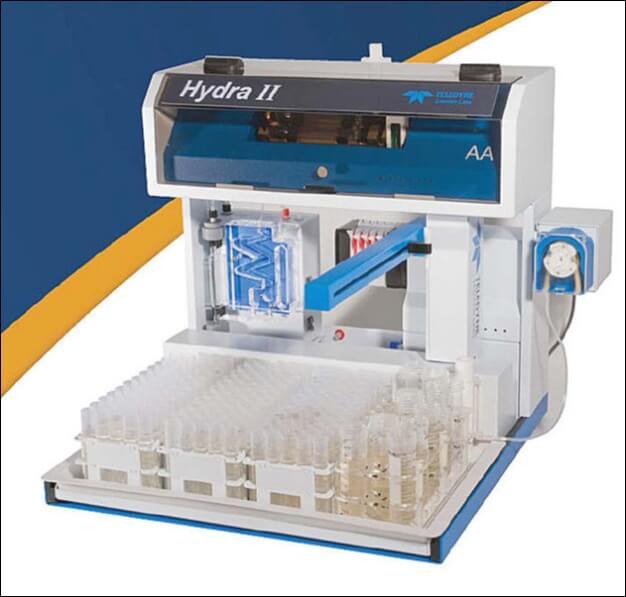
Mercury Analyzer (Leeman Labs Hydra II AA)Principle: A digestate is first prepared. Mercury in the sample is then reduced to elemental mercury by the addition of stannous chloride and measured by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Applications: Widest range of sample matrices including soil, sludge, Vegetation, tissue and difficult foaming samples, Seawater,waste water and drinking water. |
Flow Injection Analyzer (Lachat Quick Chem 8500 Series)Principle: Flow injection analysis (FIA) is based on the injection of a liquid sample into a moving, Non segmented continuous carrier stream of a suitable liquid. The injected sample forms a zone, which is then transported toward a detector that continuously records the changes in absorbance. The nitrite (which is present plus reduced nitrate) is determined by diazotization with sulfanilamide and bonding with N-(1-naphthyl)–ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (NED) to form a pink dye that is measured calorimetrically at 540 nm. The ammonia is based on the Berthelot reaction in which ammonia reacts in an alkaline solution with hypochlorite to form monochloramine, which in the presence of phenol, nitroprusside, and excess hypochlorite, gives indophenol blue. This is measured calorimetrically at 630nm. Silicate is determined as soluble silica reacts with molybdate in an acidic solution to form a yellow molybdosilicate complex. This complex is reduced with stannous chloride to form a heteropoly blue complex that is measured calorimetrically at 820nm. o-Phosphate reacts with ammonium molybdate and antimony potassium tartrate in an acidic medium to form an antimony-phospho-molybdate complex. This complex is reduced to a blue-colored complex by ascorbic acid and is measured calorimetrically at 880nm. Applications: To determine ammonia, Silicate, nitrite, o-Phosphate in water, seawater, groundwater, wastewater, and soils using the Lachat QuikChem® |
Image  Ion Chromatograph (Dionex ICS 5000)Principle: Ion chromatographic analysis of samples for fluoride, chloride, nitrite-N, bromide, nitrate-N, orthophosphate-P, and sulfate. The anions of interest are separated and measured, using a system comprised of a guard column, analytical column, suppressor device, and conductivity detector. |
Image  Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (Shimadzu TOC-V with Auto Sampler ASI-V and Solid module SSM 5000A)Principle: Inorganic carbon from carbonates and bicarbonates is removed prior to analysis by acid treatment of the sample. Then the sample is injected into the combustion tube along with a stream of O2, the organic carbon components decompose to CO2. This CO2 is detected and quantitated by the Non-Dispersive Infra-Red Detector (NDIR). Applications: TOC is the first chemical analysis to be carried out on potential petroleum source rock in oil exploration. Study and monitoring of organic contamination of rivers, lakes, dams, and other water in the natural water cycle. |
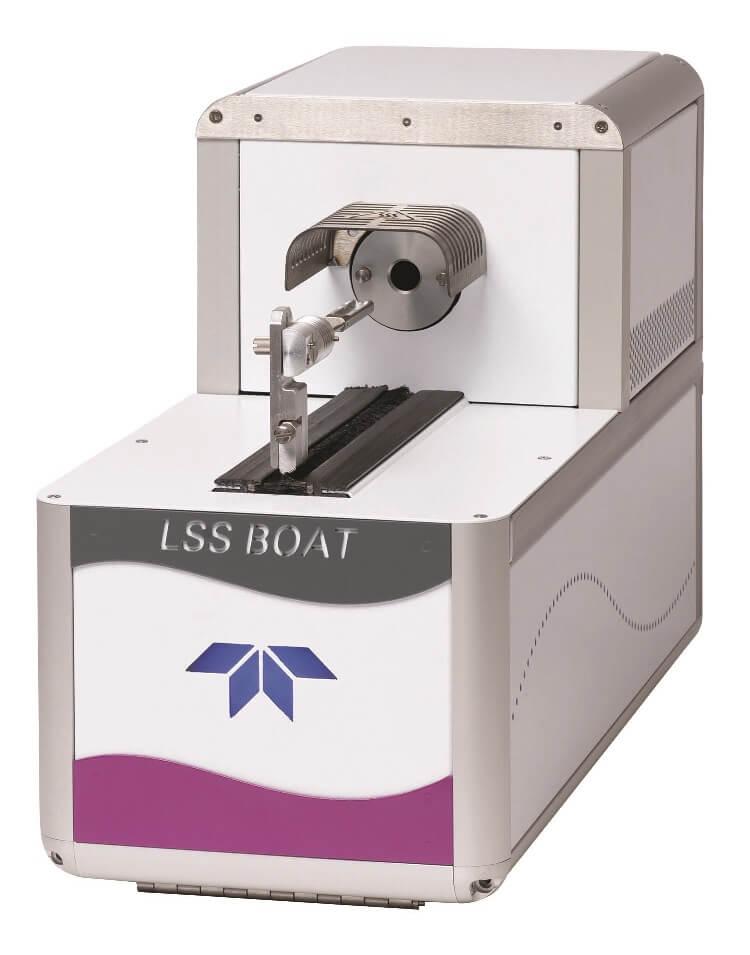
Total Organic Carbon Analyzer (Teledyne Tekmar LOTIX with Total Nitrogen analyzer and Lotix Solid Sampler – LSS Boat)Principle: The sample is combusted at temperatures up to 1,000oC. This combustion converts the nitrogen in the sample to nitric oxide. Ozone is then combined with the nitric oxide to produce an excited state of nitrogen dioxide (NO2*). As NO2* decays to its ground state, it emits light. The amount of light present is quantifiable with a chemiluminescence detector and correlates to a specific amount of nitrogen in the sample. Applications: Nitrogen monitoring can be an integral function for the process control of wastewater treatment and other industrial applications, including seawater analysis. Due to the fact that TN analysis can be performed simultaneously with traditional Total Organic Carbon (TOC) analysis, the analytical benefits can be achieved with minimal labor and capital expenditure, boosting productivity and lowering costs over existing nitrogen analysis techniques. |
Image  Discrete Analyzer Gallery Plus Aqua Master Model: Gallery Plus Aqua Master
Principle: Gallery is an automated instrument that uses enzymatic and photometric analysis principles to quickly quantify common analytes in fermentation broth samples. These analytes include ammonia, phosphate, Boron, Silicate, Alkalinity and others. The Gallery can dilute samples to appropriate ranges. Applications: To determine Boron, Silicate, Sulfide, Phosphate in water, seawater, groundwater, wastewater, and soil samples. |
Image  Basic TestsInorganic division also performs the basic tests such as pH, conductivity, turbidity, alkalinity and salinity. A pH meter provides a value as how acidic or alkaline a liquid is. (USEPA 150.1-Water, 9045C-Soil). Conductivity meter measures the electrical conductivity in a solution. (USEPA 120.1 for Soil and water). Alkalinity is the name given to the quantitative capacity of an aqueous solution to neutralize an acid. (USEPA 310.1). pH/mV meter: Fisher Scientific Accumed AB200 |
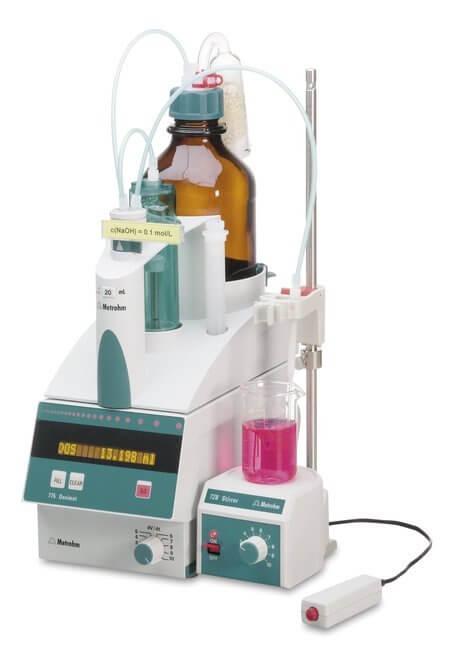
SalinityPrinciple: Titration method. The chloride ions present in the sample react with the titrant silver nitrate (AgNO3) to form silver chloride (AgCl), which gets precipitated quantitatively before potassium chromate (K2CrO4) indicator forms the brick-red silver chromate (Ag2CrO4), which is the indication of an end point of the titration. Method: SM 2520B Auto burette: MetrohmDosimat-775 |
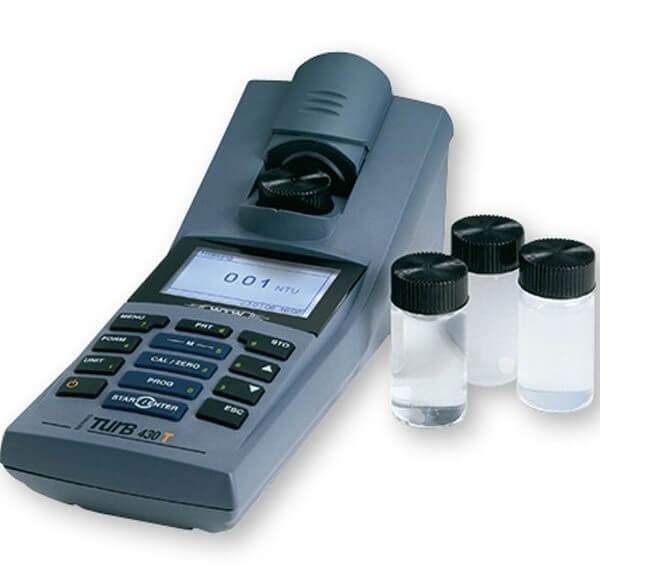
TurbidityPrinciple: The method is based upon a comparison of the intensity of light scattered by the sample under defined conditions to the intensity of light scattered by a standard reference suspension. Method: USEPA 180.1 Turbidity Meter: WTW Turb 550 IR |
Image  Melting-point apparatusPrinciple: To determine a melting point range, a small sample of the solid in close contact with a thermometer is heated in a metal heating block so that the temperature rises at a slow, controlled rate. The rate of heating would be controlled so that the melting range is as narrow as possible. Applications: organic and inorganic crystalline compounds. |
Image  Dissolved OxygenPrinciple: To measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in the water. In this bench meter we can measure BOD, OUR &SOUR parameters. Applications: water, seawater, groundwater, wastewater. |


 Colored
Colored Grayscale
Grayscale